Physics II - B14
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Magnetic Force Between Two Parallel Conductors
- Magnetic Field for a Long, Straight Conductor
- Magnetic Field for a Circular Current Loop
- Magnetic Field Lines for a Loop
- Ampere’s Law
- Long Wire with Finite Thickness
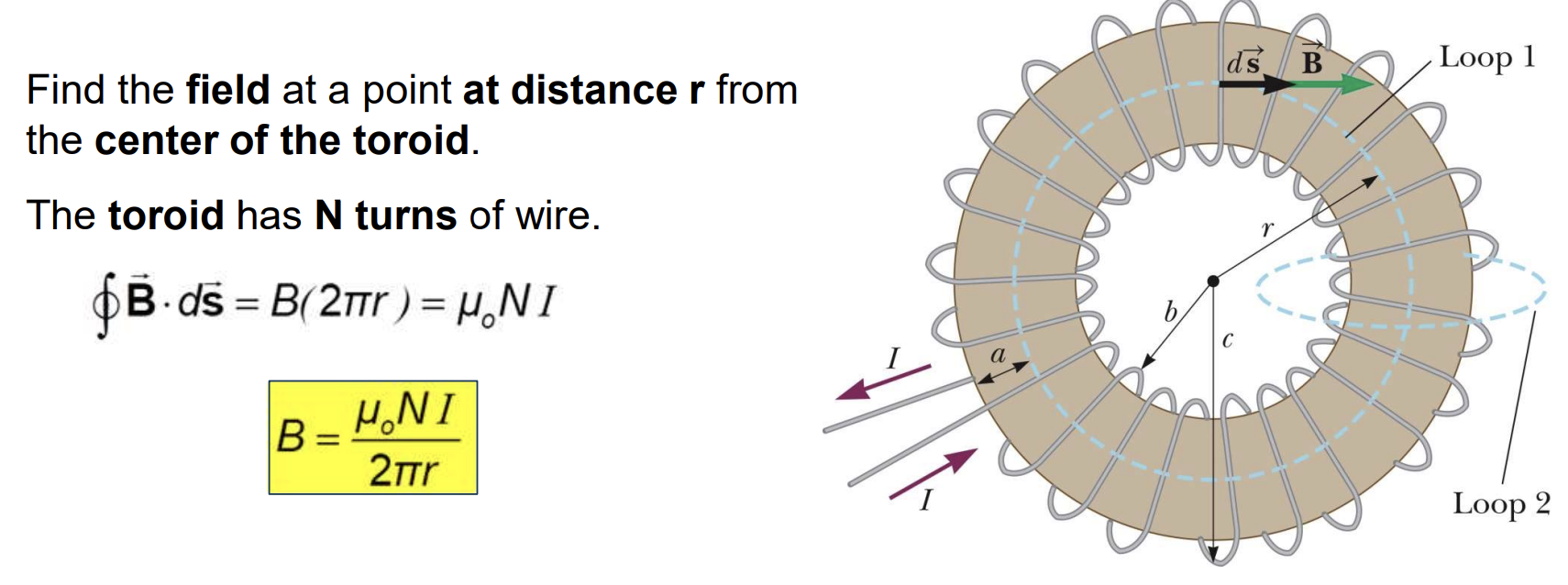
- Magnetic Field of a Toroid
- Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
Magnetic Force Between Two Parallel Conductors

$\Rightarrow$ the definition of Ampere
Parallel conductors carrying currents in the same direction attract each other, and parallel conductors carrying currents in opposite directions repel each other.
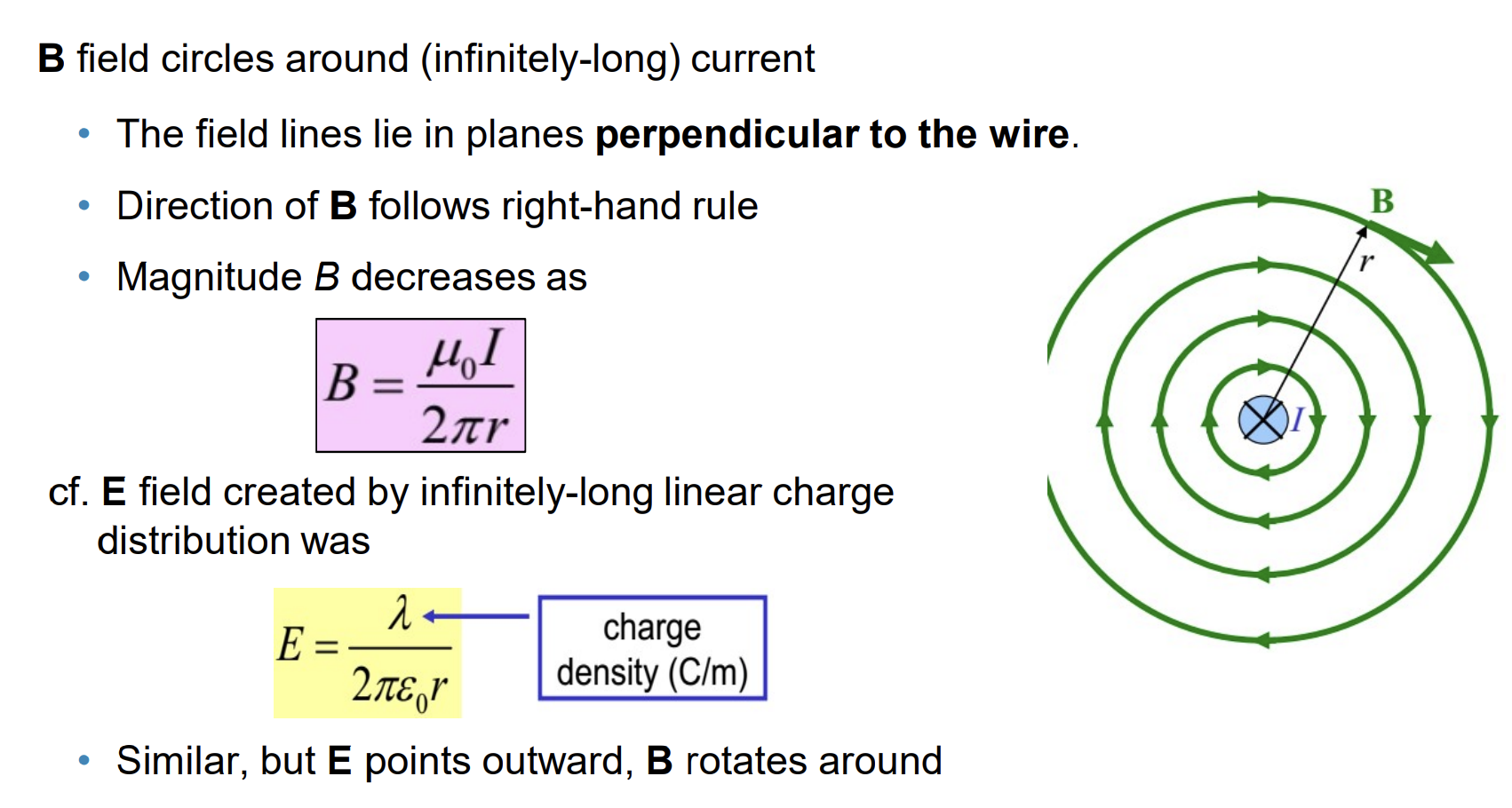
Magnetic Field for a Long, Straight Conductor
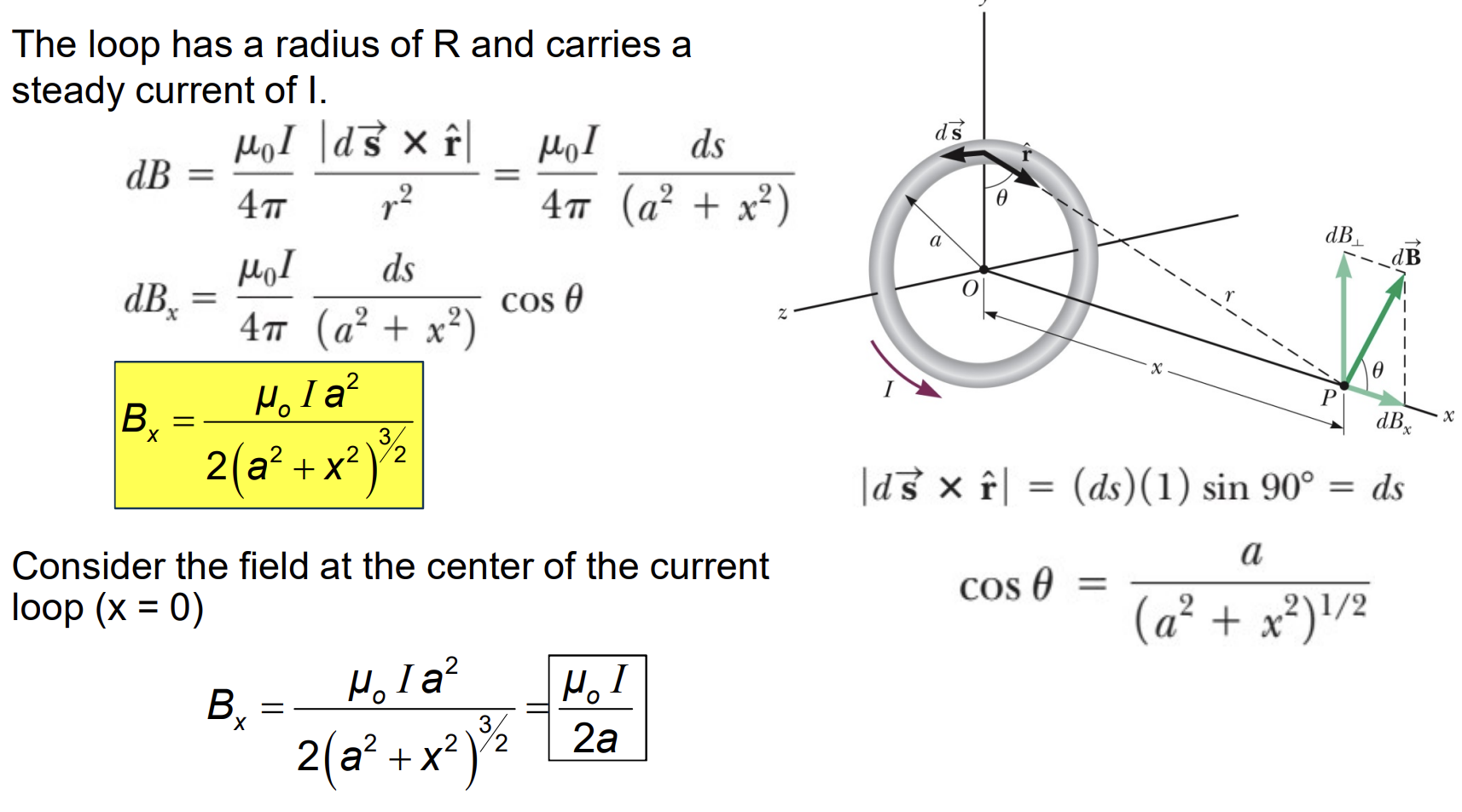
Magnetic Field for a Circular Current Loop
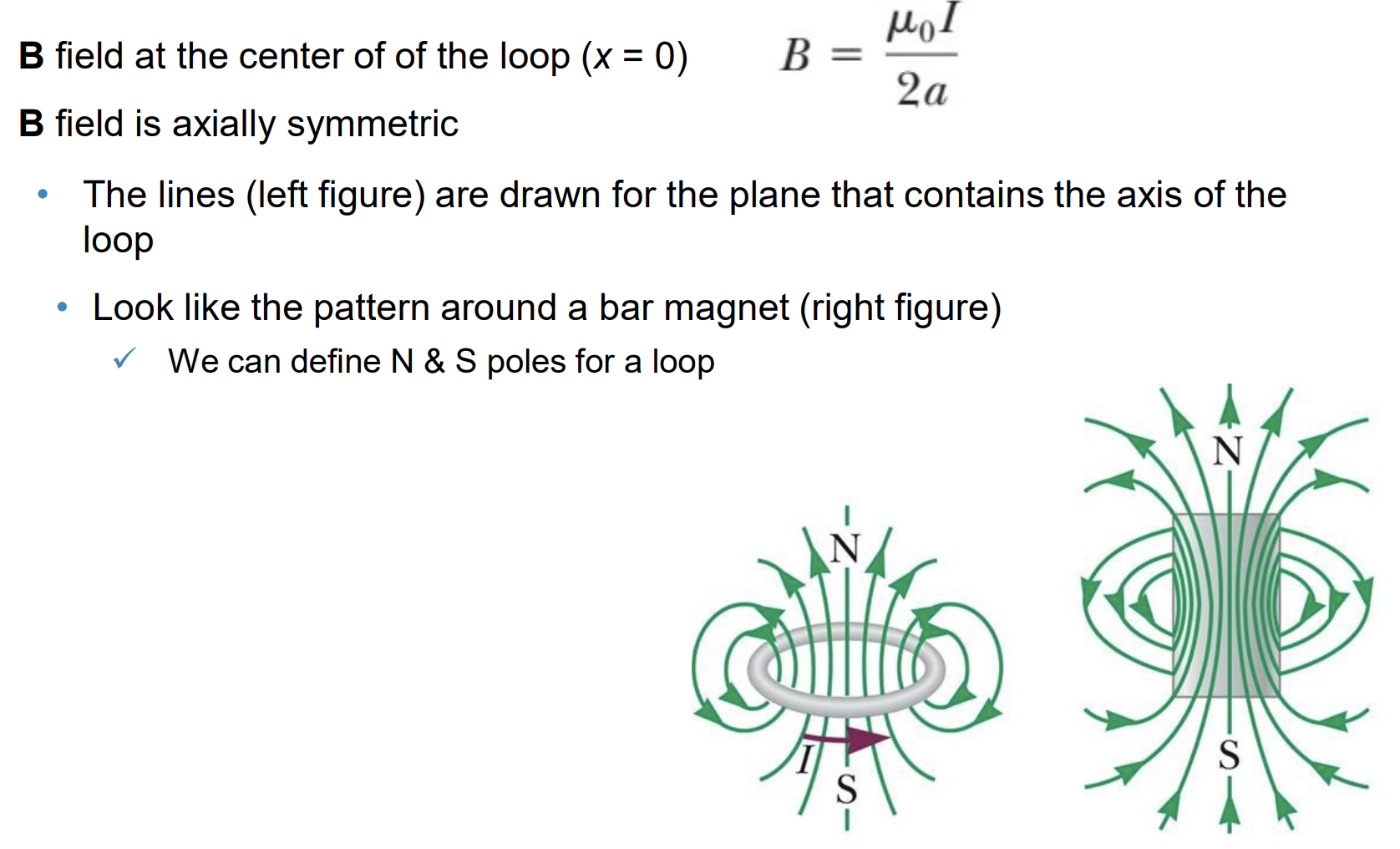
Magnetic Field Lines for a Loop
Ampere’s Law

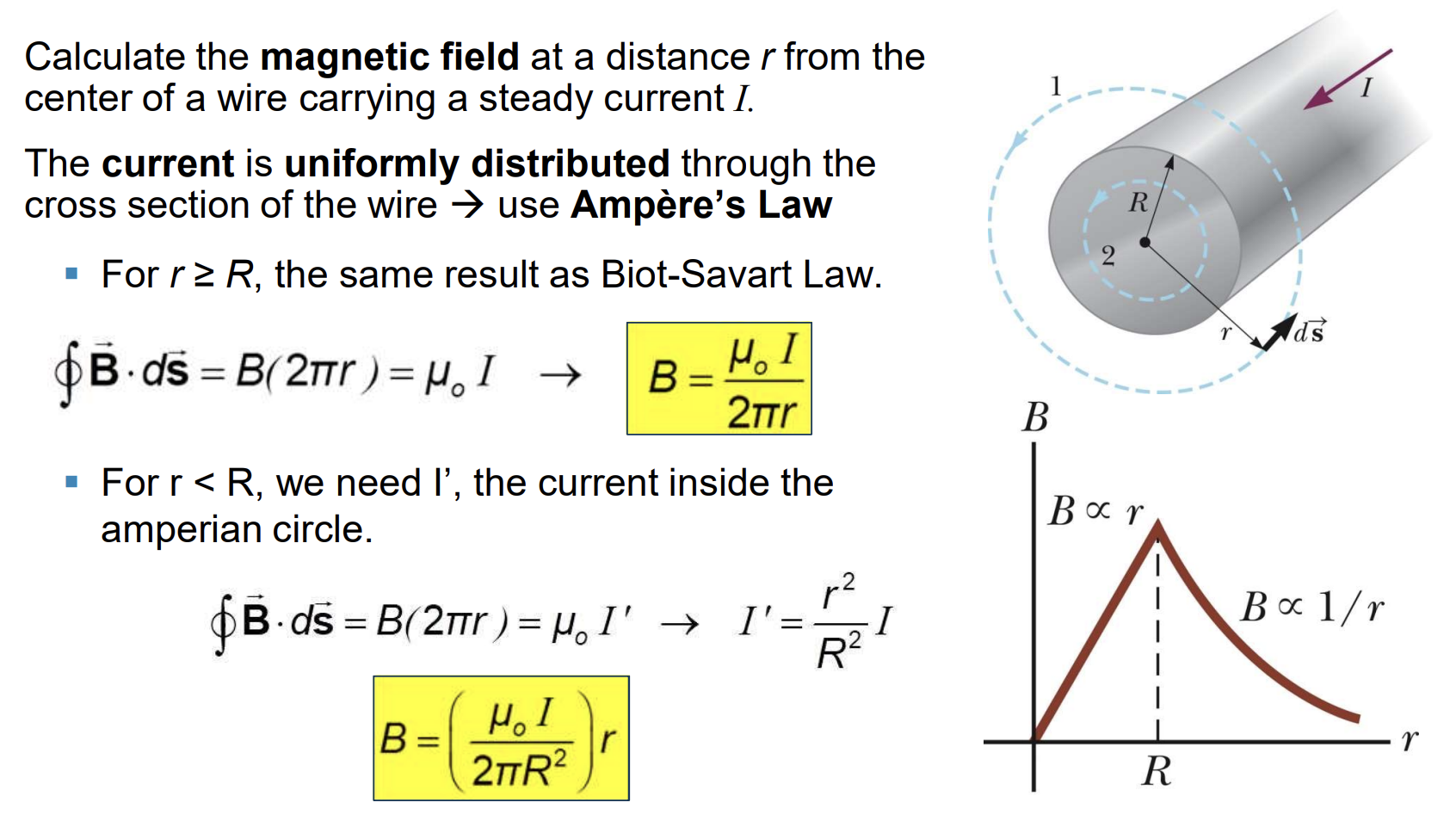
Long Wire with Finite Thickness
Magnetic Field of a Toroid
Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
- The magnetic field lines resemble that of a magnet.

- Uniform field: parallel and equally spaced

