Physics II - B03
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Electric Flux (Thông Lượng Điện)
- Gauss’s law
- Field Due to a Spherically Symmetric Charge Distribution
- New words
- Other references
Electric Flux (Thông Lượng Điện)
- Electric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular to the field.
Number of field lines $\sim$ $E.dA.cos(\vec E, \vec n) = \vec E.d\vec A$
Open Surface
\[\phi_E = \int_S \vec E. d\vec A\] \[Units: \left[\frac{N.m^2}{C}\right]\]Closed Surface
- Net lines $\sim$ $\phi_E = \oint \vec E.d\vec A$
- $\phi_E > 0 \to out > into$
Example

$\phi~total~ = 0 \to$ because electric field lines go in will go out.
Gauss’s law
\(\phi_E = \oint_S \vec E.d\vec A = \frac{q_{in}}{\epsilon_0}\)

The electric flux of these non symetric surfaces = the electric flux of sphere.
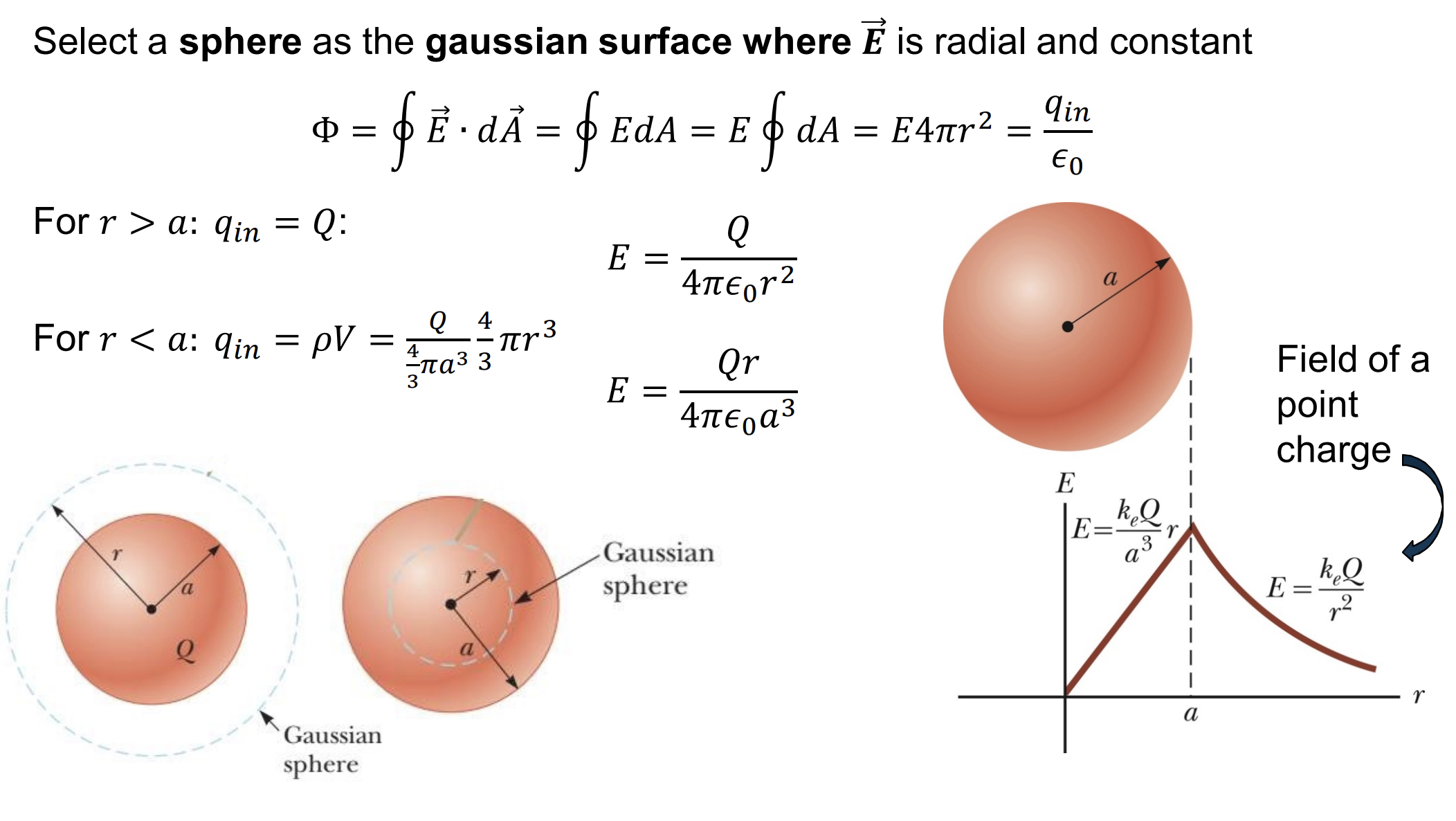
Field Due to a Spherically Symmetric Charge Distribution
New words
- hollow: rỗng
- solid: đặc