Physics II - B06
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Finding E from V
- Assignments
- Conductor in electrostatic equilibrium
- Irregularly Shaped Objects
- Notes:
- Other references
Finding E from V
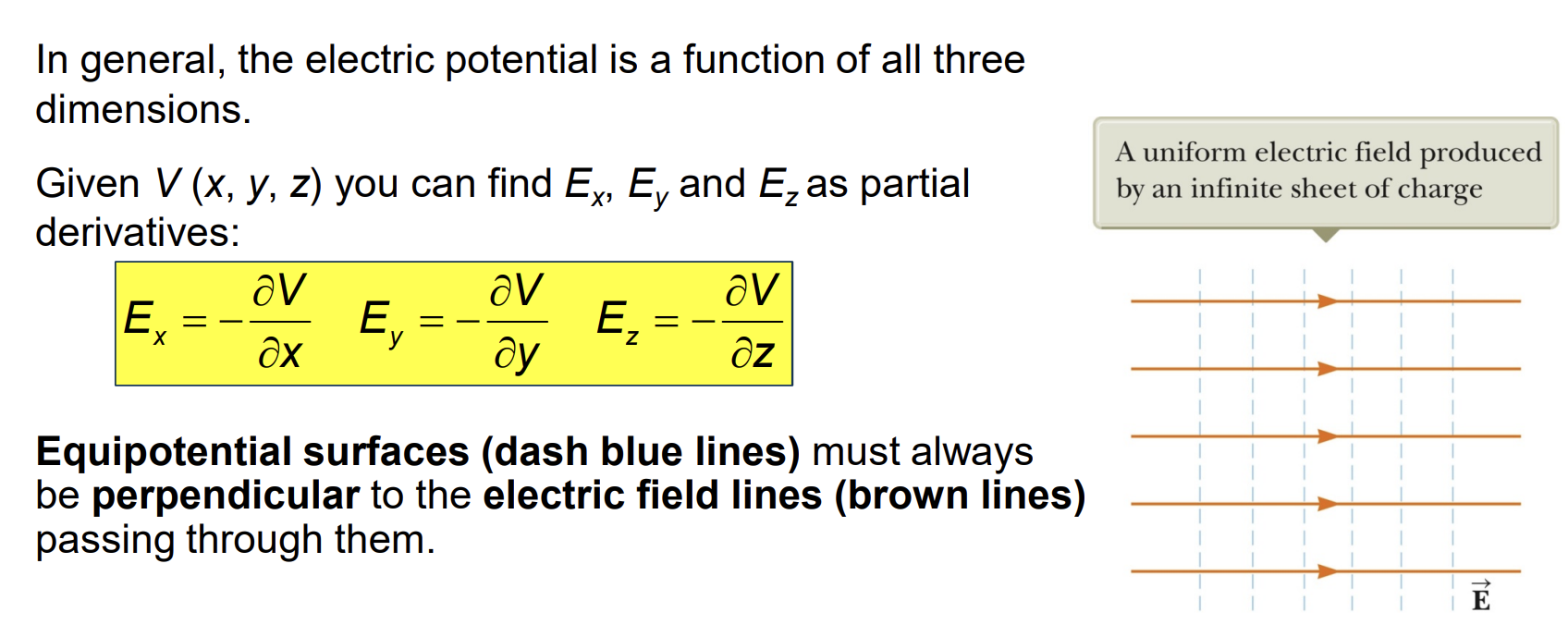
Assignments
Problem 1

Problem 2


Problem 3

$r \geqslant R:$
\[\displaystyle \Delta V = -\int_A^B \vec E.d \vec s = -\int_A^B E.dr\] \[= -\frac{Q}{4\pi.\epsilon_0}.\bigg(\frac{1}{r_a} - \frac{1}{r_b}\bigg)\] \[V_{\infty} = 0 \to V(r) = \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}.\frac{Q}{r}\]Conductor in electrostatic equilibrium
- $\vec E_{inside} = 0$
- $V_{inside} = const$
- $\Delta V= 0$ between any two points on the surface.
- Extra charges on the surface. Notes: $\vec E$ is vertical because if not, it will create an angle so it will have the tangent component so it will move which is illogical with “electrostatic” (No moving charges) $\to \vec E \bot$ surface

Irregularly Shaped Objects

- Nguyên lý hoạt động của cột ngư lôi
- Vì vật nhọn thì $\sigma$ sẽ lớn $\to E$ lớn $\to q$ lớn $\to$ dễ tích điện.
Notes:
- Solid sphere $\to$ insulating.
- If conductor $\to$ charges on surface.